
Blog
Basic 3D Printing Terms Every Beginner Should Know
Basic 3D Printing Terms Every Beginner Should Know
1. Basic 3D Printing Terms: What is FDM?
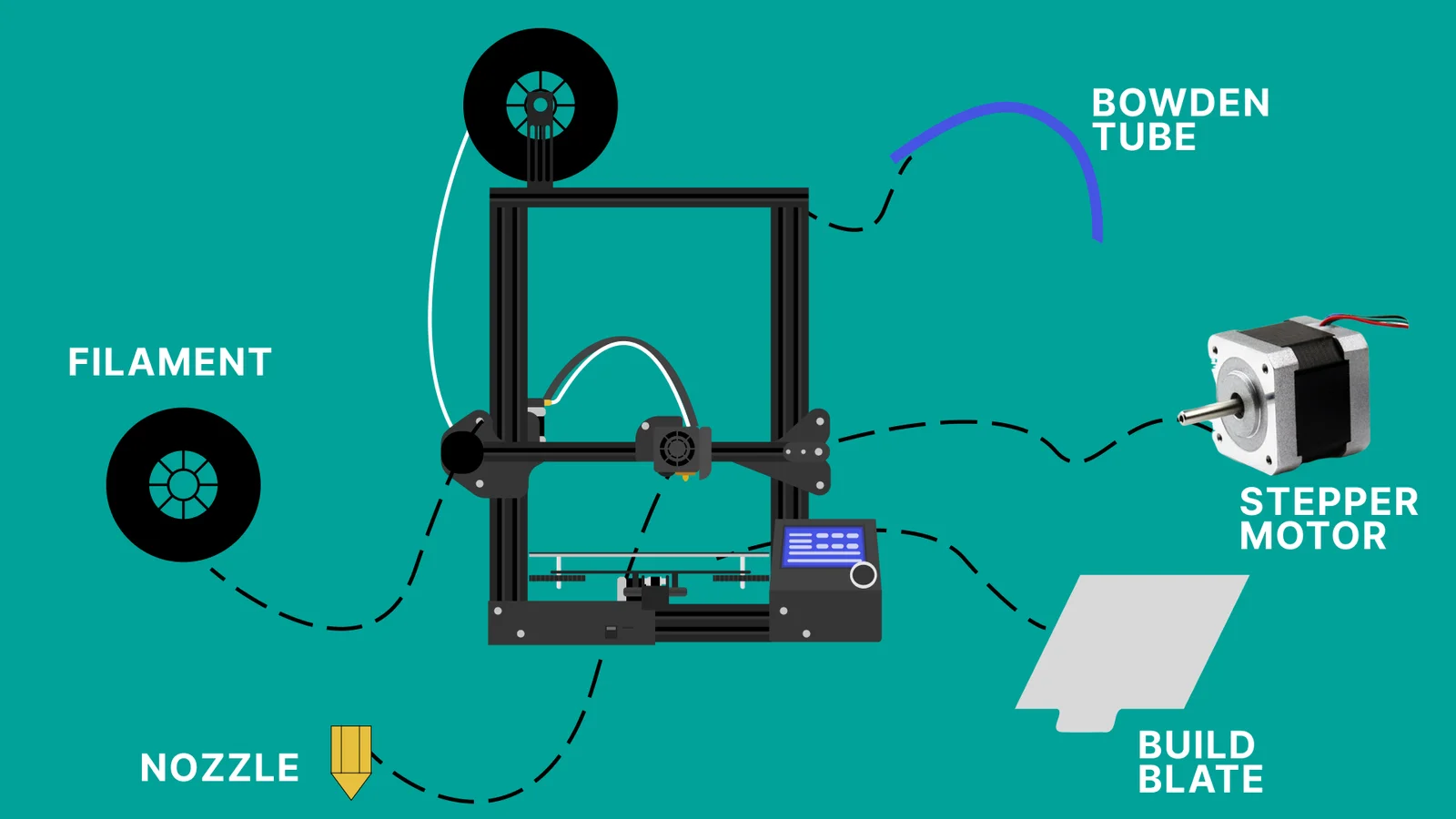
Filament is the plastic material used in FDM printers. It comes in spools and typically measures 1.75mm in diameter.
PLA (Polylactic Acid)
-
Beginner-friendly
-
Easy to print
-
Low warping
-
Biodegradable
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene)
-
Strong and heat-resistant
-
Requires heated bed
-
Can warp easily
PETG
-
Stronger than PLA
-
More flexible
-
Good chemical resistance
For beginners learning Basic 3D Printing Terms, PLA is usually the best starting material.
You can explore material comparisons on All3DP (DoFollow):
https://all3dp.com
3. Basic 3D Printing Terms: What is a Slicer?
A slicer is software that converts a 3D model into printer instructions.
It:
-
Divides models into layers
-
Generates G-code
-
Allows you to control print settings
Popular slicers include:
-
Cura
-
PrusaSlicer
You can download Cura from its official site (DoFollow):
https://ultimaker.com/software/ultimaker-cura
4. Basic 3D Printing Terms: G-code Explained
G-code is the language your printer understands.
It tells your printer:
-
Where to move (X, Y, Z)
-
When to extrude filament
-
What temperature to use
-
How fast to print
When you click “Slice,” your slicer generates a G-code file that your printer executes line by line.
Understanding this term is fundamental when learning Basic 3D Printing Terms because every print depends on it.
5. Basic 3D Printing Terms: Layer Height
Layer height refers to how thick each printed layer is.
Smaller Layer Height (0.1mm)
-
More detail
-
Smoother finish
-
Longer print time
Larger Layer Height (0.3mm)
-
Faster prints
-
Less detail
-
Visible layer lines
A 0.2mm layer height is the standard beginner setting.
6. Basic 3D Printing Terms: Infill
Infill is the internal structure inside a printed object.
Most prints are not solid — they contain patterns to reduce material usage.
Infill Percentage
-
0%: Hollow
-
20%: Standard strength
-
50%+: Strong parts
-
100%: Solid
Infill Patterns
-
Grid
-
Honeycomb
-
Gyroid
Infill is one of the most important Basic 3D Printing Terms because it affects strength and print time significantly.
7. Basic 3D Printing Terms: Bed Leveling
Bed leveling ensures that the nozzle is the correct distance from the print surface.
If the nozzle is:
-
Too close → Filament gets squished
-
Too far → Poor adhesion
-
Uneven → Failed print
Proper bed leveling is essential for successful printing.
If you want a step-by-step setup guide, check our internal guide here:
How to Set Up Your First 3D Printer
8. Basic 3D Printing Terms: Nozzle
The nozzle is the small metal tip where filament exits.
Common Sizes
-
0.4mm (standard)
-
0.2mm (detail)
-
0.6mm+ (faster printing)
Nozzle size directly impacts print resolution and speed.
9. Basic 3D Printing Terms: Supports
Supports are temporary printed structures that hold up overhanging parts.
They:
-
Prevent sagging
-
Are removed after printing
-
May leave small marks
Good model orientation reduces the need for supports.
For advanced support settings, you can also read our internal post:
3D Printing Troubleshooting Guide
10. Basic 3D Printing Terms: Retraction
Retraction pulls filament back slightly when the nozzle moves without printing.
Without proper retraction:
-
Strings form between parts
-
Prints look messy
Retraction tuning improves surface quality.
11. Basic 3D Printing Terms: Warping
Warping happens when corners lift from the print bed.
Causes
-
Uneven cooling
-
Poor adhesion
-
No heated bed
-
Drafts
Solutions
-
Use a heated bed
-
Add a brim
-
Improve leveling
-
Use adhesive
Warping is especially common with ABS.
12. Basic 3D Printing Terms: Brim, Raft, and Skirt
These are adhesion helpers.
Skirt
Printed around the model, not touching it.
Used to prime the nozzle.
Brim
Attached to the base.
Improves adhesion.
Raft
Printed under the model entirely.
Used for difficult prints.
Final Thoughts on Basic 3D Printing Terms
Learning Basic 3D Printing Terms is the foundation of successful 3D printing. Once you understand what each setting means, you can troubleshoot problems faster and improve print quality.
Start simple:
-
Use PLA
-
Set layer height to 0.2mm
-
Keep infill around 20%
-
Focus on good bed leveling
From there, you can experiment with advanced materials and fine-tune your settings.









